Under the Microscope
Latest Research News
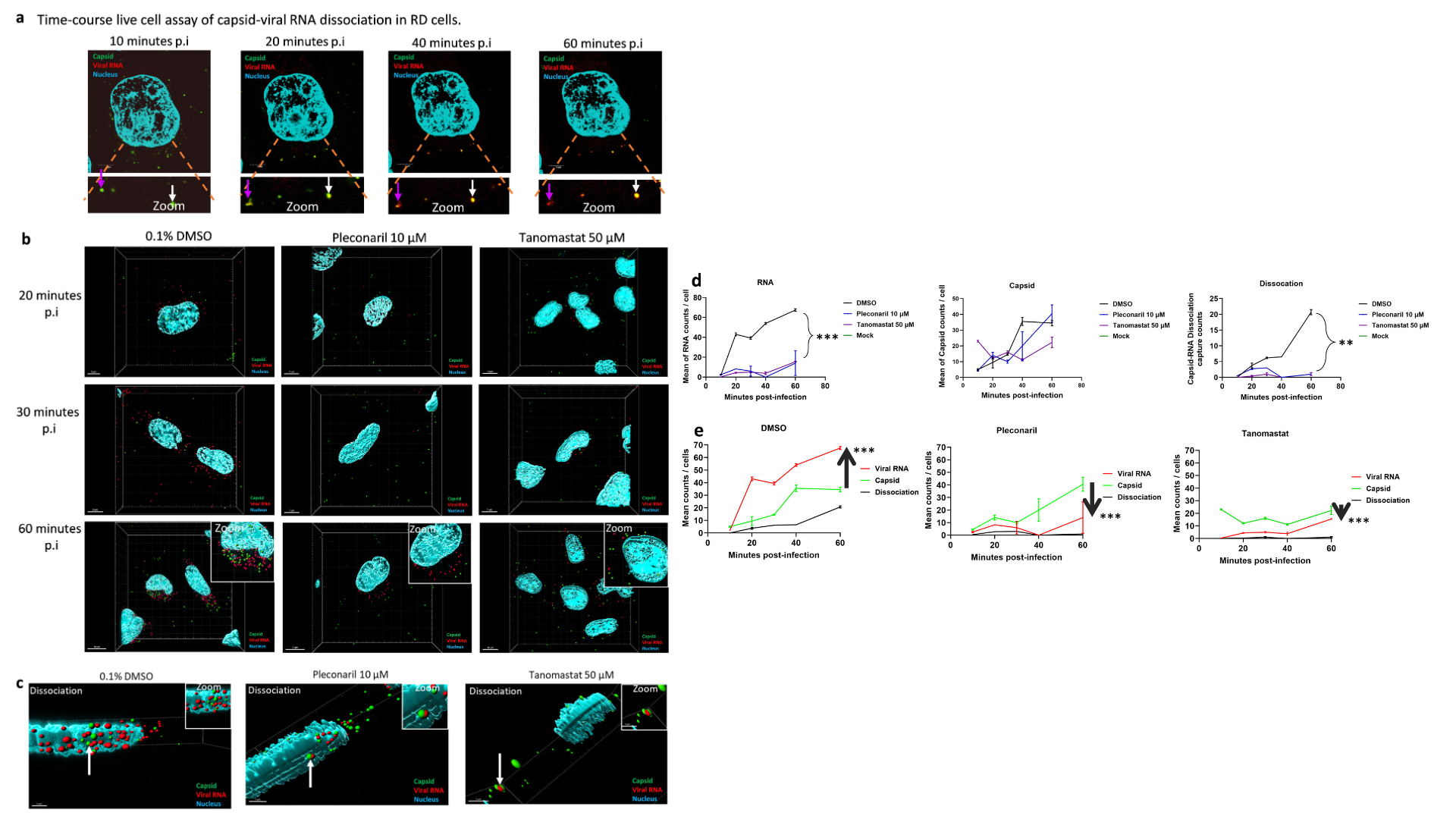
Figure 4. Tanomastat limits capsid-viral RNA dissociation upon internalization of EV-A71 into RD cells. (a) Time-course live cell assay of capsid-viral RNA dissociation was observed for a prolonged period of 60 minutes post-infection at M.O.I of 20. Tracking of single viral capsid showed dissociation of the capsid (green) and release of viral RNA (red). Overlapping viral RNA and capsid (yellow) indicates the start of dissociation. The purple/white arrows over the time course tracks a single virus particle up to capsid-viral RNA dissociation. (b) Snapshot of time-course live cell assay of capsid and viral RNA intracellular at 20-, 30-, and 60-minutes post-infection at M.O.I of 20. 10 µM Pleconaril served as capsid-viral RNA dissociation inhibitor positive control. Images were processed using Imaris 10·1 software indicated by capsid (green), viral RNA (red), and nucleus (blue). (c) Capsid-viral RNA dissociation is indicated by colocalization of capsid to viral RNA with a distance of less than or equal to 1 µm (white arrow). (d) Mean of viral RNA, capsid and viral particle dissociation counts for 0·1% DMSO, positive control, pleconaril, and 50 µM Tanomastat treatment upon infection at M.O.I of 20. (e) 0·1% DMSO, positive control, pleconaril, and 50 µM Tanomastat treatment upon infection at M.O.I of 20. Green arrow indicates lower or higher mean viral RNA to mean viral capsid counts. Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test was used to determine the statistical significance of the treatments when compared against 0.1% DMSO vehicle control. P-values, mean difference, and 95% CI are reported in Table S4. Line graphs represent mean±standard deviation with * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001.
Lim TYM, Jaladanki CK, Wong YH, Yogarajah T, Fan H, Chu JJH. Tanomastat exerts multi-targeted inhibitory effects on viral capsid dissociation and RNA replication in human enteroviruses. EBioMedicine. 2024 Sep;107:105277. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105277. Epub 2024 Sep 2. PMID: 39226680; PMCID: PMC11419895.
