Oesophageal cancer
Oesophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer overall world-wide (1). In Singapore, oesophageal cancer is uncommon. Despite this, cancer of the oesophagus has very poor survival, making it the sixth most common cause of death from cancer worldwide and the tenth most common of cause of death from cancer among Singaporean Men (2).
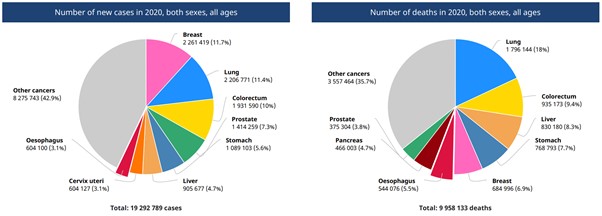
Figure 1: Global incidence and mortality from Oesophageal Cancer (Source: GLOBOCAN 2020)
Due to the lack of a national screening program for oesophageal cancer, most patients present only when symptomatic. As such, a large majority of patients present at an advanced stage (Stage III or IV).
Symptoms of Oesophageal Cancer include:
- Difficulty or pain on swallowing
- Unintentional weight loss
- Chest pain/discomfort/pressure/burning
- Hoarseness of voice or coughing
- Vomiting or regurgitation
- Bleeding (vomiting blood or passing black stools)
- Early stages of oesophageal cancer typically cause no signs or symptoms.
Risk factors for oesophageal cancer include:
- Male gender
- Age - > 50 years old
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Obesity
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Drinking very hot liquids regularly
- Pre-existing conditions such as Achalasia and Barrett’s oesophagus
Diagnosis
Endoscopy is the best investigation for diagnosis, with high accuracy. It is very safe, quick and simple, being a fibreoptic camera examination of the oesophagus and stomach under sedation as an ambulatory day procedure.
Computed tomography scans (CT scans), Positron emission tomography – Computed tomography (PET/CT) scans, bronchoscopy and endoscopic ultrasonography may be performed to further evaluate if oesophageal cancer is diagnosed.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer. Options of treatment include:
- Endoscopic or surgical removal of the cancer
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Tube placement, oesophageal stenting
- Combination of the above treatment options
Our team offers a comprehensive range of treatment options for patients, and strives to perform minimally invasive surgery where possible.
References:
- GLOBOCAN 2020: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/6-Oesophagus-fact-sheet.pdf
- Singapore Cancer Registry 2018 annual report: https://www.nrdo.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider3/default-document-library/scr-annual-report-2018.pdf?sfvrsn=bcf56c25_0
Research
Given the poor prognosis and outcomes for oesophageal cancer patients as compared to other cancers, there is an urgent need to improve. Our UGI unit strives to perform high quality research to improve patient outcomes. As a tertiary hospital, we also collaborate with international centres of excellence to better study and treat this disease.
Ongoing Research
- Distribution of lymph node metastases in esophageal carcinoma: TIGER study
The aim of this study is to determine the distribution of lymph node metastases in patients with resectable esophageal or gastro-esophageal junction carcinoma in whom a transthoracic esophagectomy with a 2- or 3-field lymphadenectomy is performed. This can be the foundation for a uniform worldwide staging system and establishment of the optimal surgical strategy for esophageal cancer patients.
- Benchmarking Complications Associated with Esophagectomy
Utilizing a standardized dataset with specific definitions to prospectively collect international data to provide a benchmark for complications and outcomes associated with esophagectomy.
Recent Publications
- Outcomes after totally minimally invasive versus hybrid and open Ivor Lewis oesophagectomy: results from the International Esodata Study Group.
van der Wilk BJ, Hagens ERC, Eyck BM, Gisbertz SS, van Hillegersberg R, Nafteux P, Schröder W, Nilsson M, Wijnhoven BPL, Lagarde SM, van Berge Henegouwen MI; International Esodata Study Group Collaborators.
Br J Surg. 2022 Jan 13:znab432. doi: 10.1093/bjs/znab432. Online ahead of print.
PMID: 35024794 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35024794/
- Outcomes of oesophageal cancer treated with neoadjuvant compared with definitive chemoradiotherapy.
Wujanto C, Tey J, Vellayappan B, So J, Yong WP, Shabbir A, Tseng M, Soon YY, Ho F.
Ann Acad Med Singap. 2021 Jul;50(7):536-547. doi: 10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.2020633.
PMID: 34342334
- Risk Prediction Model of 90-Day Mortality After Esophagectomy for Cancer.
D'Journo XB,.., So JB, .., Thomas PA, Low DE; International Esodata Study Group.
JAMA Surg. 2021 Sep 1;156(9):836-845. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.2376.
PMID: 34160587
Sundar R; Ng A; Zouridis H; Padmanabhan N; Sheng T; Zhang S; Lee MH; Ooi WF; Qamra A; Inam I; Hewitt LC; So JB-Y; Koh V; Nankivell MG; Langley RE; Allum WH; Cunningham D; Rozen SG; Yong WP; Grabsch HI; Tan P
European Journal Of Cancer, 2019 Dec;123, 48-57. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.09.016.
PMID: 31655359

