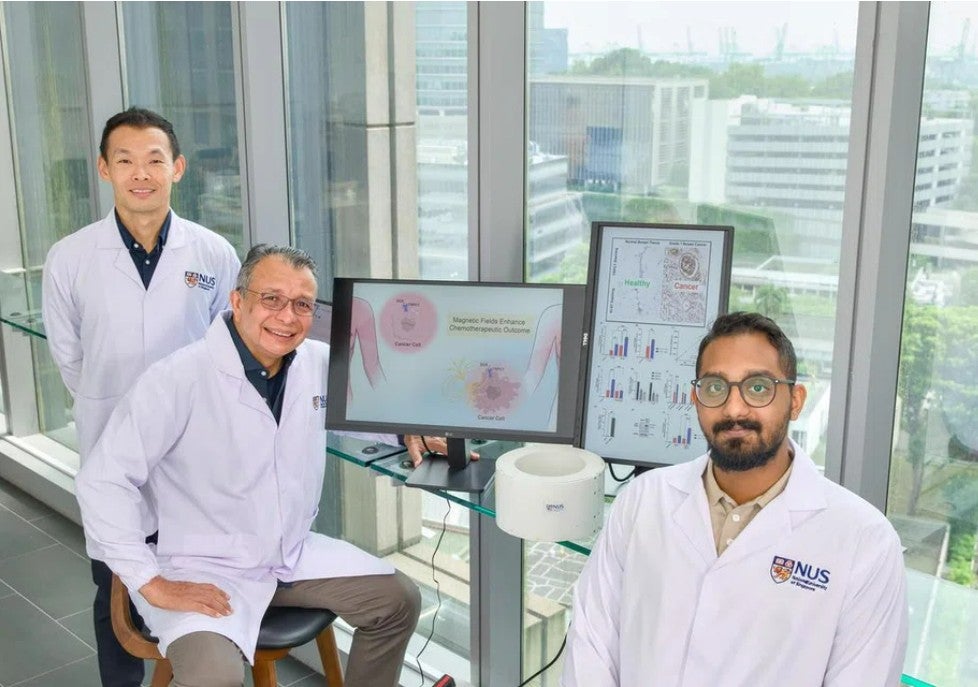
Chemotherapy, although the first line of defense in cancer treatment, is indiscriminate and is damaging to the entire body, which, ironically, worsens a patient’s chances of getting better from cancer. Doxorubicin is a widely used chemotherapy drug for breast cancer but has significant side effects due to its systemic delivery.
This study led by N2CR member A/Prof Alfredo Franco-Obregon with co-first authors, Viresh Krishnan Sukumar (N2CR PhD Scholarship student) and Dr Alex Tai Yee Kit, found that a 10-minute magnetic exposure increases doxorubicin uptake in breast cancer cells without harming the surrounding healthy cells. The study suggests a localized, non-invasive magnetic therapy to enhance doxorubicin efficacy with fewer side effects. This may ultimately allow for the lowering of systemic doxorubicin administration that could improve a patient’s outcome against cancer. This would be a potential game changer in cancer treatment.
Click here to read on Straits Times.
Click here to read on NUS News.
Click here to read research article.