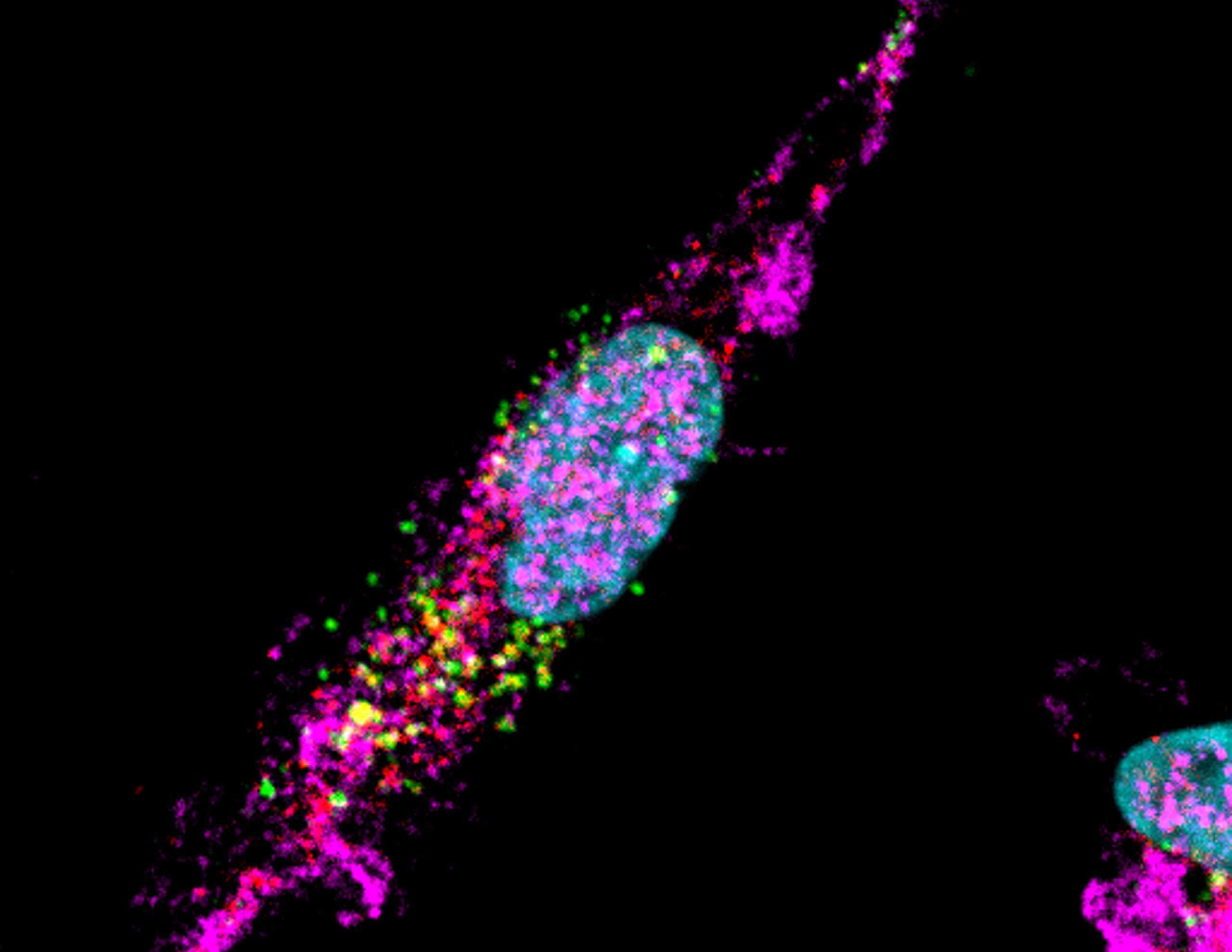
Assistant Professor Minh Le from the Department of Pharmacology and the Institute for Digital Medicine (WisDM), Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), led the study that demonstrated that the uptake of RBCEVs by macrophages was highly efficient, as the particles induced multiple changes in the macrophages.