
The neuropeptide relaxin-3 is composed of an A chain and a B chain held together by disulfide bonds, and it modu- lates functions such as anxiety and food intake by binding to and activating its cognate receptor RXFP3, mainly through the B chain. Biased ligands of RXFP3 would help to determine the molecular mechanisms underlying the
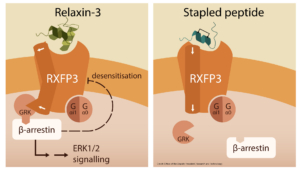
activation of G proteins and β-arrestins downstream of RXFP3 that lead to such diverse functions. We showed that the i, i+4 stapled relaxin-3 B chains, 14s18 and d(1-7)14s18, were Gαi/o-biased agonists of RXFP3. These peptides did not induce recruitment of β-arrestin1/2 to RXFP3 by GPCR kinases (GRKs), in contrast to relaxin-3, which enabled the GRK2/3-mediated recruitment of β-arrestin1/2 to RXFP3. Relaxin-3 and the previously reported peptide 4 (an i, i+4 stapled relaxin-3 B chain) did not exhibit biased signaling. The staple linker of peptide 4 and parts of both the A chain and B chain of relaxin-3 interacted with extracellular loop 3 (ECL3) of RXFP3, moving it away from the
binding pocket, suggesting that unbiased ligands promote a more open conformation of RXFP3. These findings highlight roles for the A chain and the N-terminal residues of the B chain of relaxin-3 in inducing conformational changes in RXFP3, which will help in designing selective biased ligands with improved therapeutic efficacy.
Image credit: Office of the Deputy President (Research and Technology)
Full article:https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.abl5880
