Definition:
Cell injury: Sequence of events that occurs when stresses exceed ability of cells to adapt. Responses are initially reversible, but may progress to irreversible injury and cell death.
Cell death: Results when continuing injury becomes irreversible, at which time the cell cannot recover.
There are TWO principle types of cell death:
- 1. Necrosis - Death of cells in living tissues characterized by the breakdown of cell membranes. These changes occur because of digestion and denaturation of cellular proteins, largely by release of hydrolytic enzymes from damaged lysosomes.
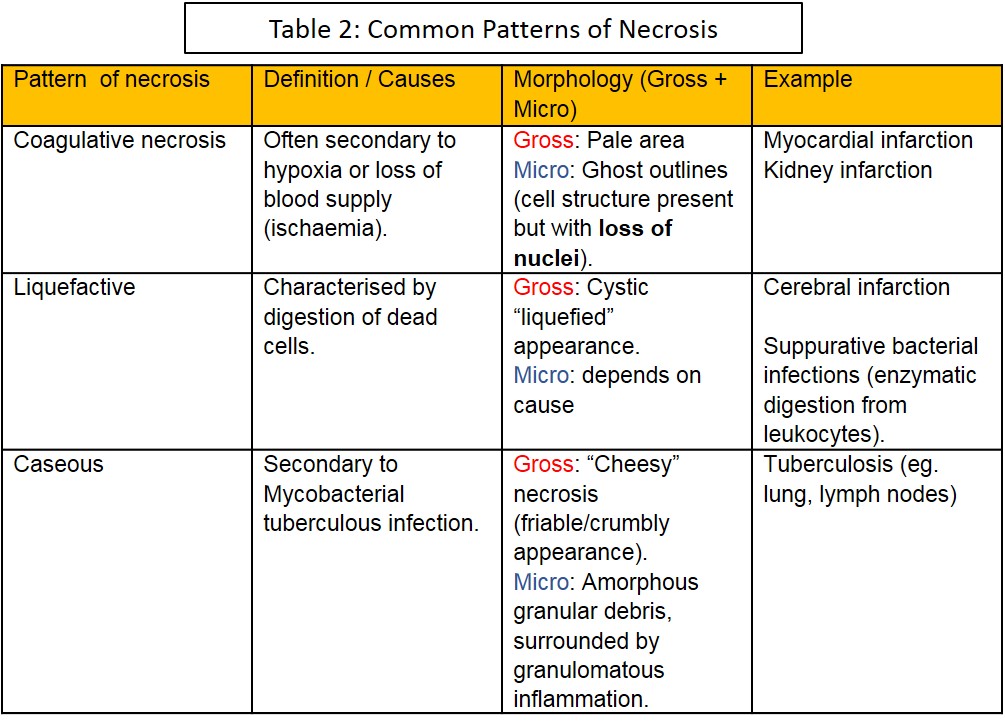
There are many subtypes / morphological patterns of necrosis: Coagulative; Liquefactive; Caseous; ;
Haemorrhagic; Suppurative; Gangrenous; Fat; Fibrinoid
- 2. Apoptosis - Defined as programmed cell death characterized by nuclear dissolution, fragmentation of the cell without complete loss of membrane integrity, and rapid removal of the cellular debris.
Apoptosis can be physiological or pathological
Mindmap: Cell Injury and Death
If you can't play the video, watch it here on YouTube: https://youtu.be/DGwG4TQwVec
Mindmap: Causes and Mechanisms
If you can't play the video, watch it here on YouTube: https://youtu.be/2XpMVxK94kM
Mindmap: Morphology
If you can't play the video, watch it here on YouTube: https://youtu.be/A7IsBseAVas